Beijing, as the capital of China, is a populous city with an extensive and complex transportation network. To facilitate commuting for residents and visitors alike, the Beijing Subway system operates more than 20 lines with a daily ridership in the tens of millions.
This guide offers an overview of the major lines, the areas they serve, fare ranges, and detailed instructions for first-time users.
Main Lines and Coverage
Below is a summary of key lines, their routes, major stations, termini, fares, and the main districts they traverse:
| Line | Color | One-Way Fare (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Line 1 | Red | ¥3–6 |
| Line 2 | Dark Blue | ¥3–6 |
| Line 4 | Light Blue | ¥3–7 |
| Line 5 | Purple-Red | ¥3–7 |
| Line 6 | Light Brown | ¥3–8 |
| Line 7 | Orange | ¥3–7 |
| Line 8 | Green | ¥3–8 |
| Line 10 | Light Blue | ¥3–8 |
| Line 13 | Yellow | ¥3–6 |
| Line 14 | Pink | ¥3–8 |
| Line 15 | Purple | ¥3–8 |
| Airport Express | Light Blue | ¥25 |
Note: Beijing Subway fares are distance-based. The starting price is generally ¥3 for up to 6 km, and approximately ¥1 is added for every additional 10 km. The maximum fare for long-distance rides is generally no more than ¥10 (the Airport Express Line is priced separately).
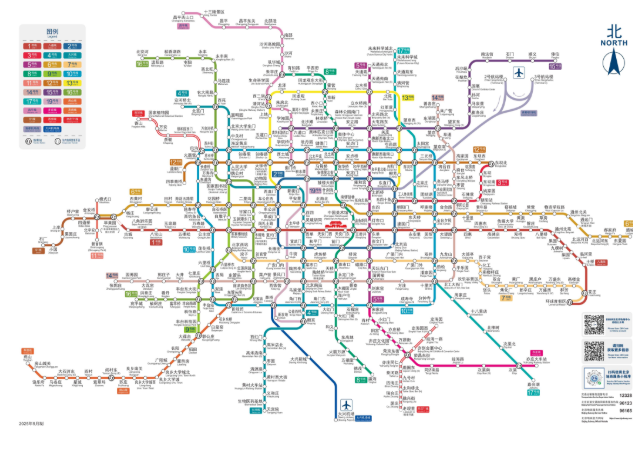
Beijing Subway Map
We’ve prepared a Beijing subway line chart for you, which you can download to familiarize yourself with the entire network.
Next, we will provide detailed information about the key attractions to watch for along each subway line.
| Subway Line | Famous Landmarks | Approximate Walking Time from Exit |
|---|---|---|
| Line 1 | Tiananmen Square | Immediately at exit (about 1–3 min) |
| Forbidden City | 5–10 minutes walk from Tiananmen East/West Station | |
| Wangfujing Shopping Street | About 5 minutes walk | |
| Sidan Shopping Area | Immediately at exit (about 2–3 min) | |
| Line 2 | Qianmen Street | About 3–5 minutes walk |
| Zhengyangmen | About 5 minutes walk | |
| Yonghegong Lama Temple | About 3–5 minutes walk | |
| Confucius Temple | About 5–8 minutes walk | |
| Line 4 | Houhai | About 8–12 minutes walk |
| Shichahai | About 8–12 minutes walk | |
| National Library | Immediately at exit (about 2–3 min) | |
| Line 5 | Wangfujing | About 5 minutes walk |
| Longhaigong | About 3–5 minutes walk | |
| Line 6 | Dunxi Hutong | About 5–8 minutes walk |
| Nanluoxiang | About 3–5 minutes walk | |
| Line 7 | Beijing Museum of Natural History | About 5 minutes walk |
| Line 8 | Nanluoxiang | About 3–5 minutes walk |
| Olympic Park (Bird’s Nest, Water Cube) | About 5–8 minutes walk | |
| Line 10 | Sanlitun | About 10–15 minutes walk |
| Chaoyang Park | About 8–12 minutes walk | |
| Tongren District (CBD) | Immediately at exit (about 2–3 min) | |
| Line 13 | East Gate of Peking University | About 5–8 minutes walk |
| Beijing Zoo | About 5 minutes walk | |
| Line 14 | East Gate of Temple of Heaven | About 5 minutes walk |
| Fangzhuang (Food Street) | About 5–8 minutes walk | |
| Line 15 | Wangjing Soho | About 5 minutes walk |
How to Ride the Beijing Subway
If you are using the Beijing Subway for the first time, follow these steps:
1. Locate the Station Entrance
Tip for Large Transfer Stations: In major interchange stations, entrances can be spread out across a large area. Plan ahead to choose the correct entrance to avoid walking extra distances, especially during peak hours.
Look for Clear Subway Signs: Every Beijing subway station entrance is clearly marked with the official “Subway” logo—a distinctive blue and white “M” symbol—and large, visible signs that often say “Subway” or “Metro.”
These signs are usually placed above or near the entrance, making them easy to spot from a distance.
Entrance and Exit Codes: Each station has multiple entrances and exits labeled with letters such as A, B, C, or D.

These codes help you identify which entrance leads closest to your destination or transfer point.
Confirm Your Exit in Advance: Before heading out, use the official subway app, online maps, or station guides to check which entrance or exit you should use. This can save you time and avoid unnecessary walking or confusion once you arrive.
Types of Entrances: Most entrances consist of stairs, but many stations also provide escalators and elevators (accessible entrances) for passengers with luggage, strollers, or mobility challenges.

Check Nearby Landmarks and Signs: Subway entrances often have signs indicating nearby streets, buildings, or landmarks to help confirm you’re at the right entrance.
Buy a Ticket or Scan to Enter
To purchase a subway ticket in Beijing, first locate a ticket vending machine, which can usually be found near station entrances. On the machine’s touchscreen, select the option labeled “Buy Ticket” or “Single Journey Ticket.” Next, either select your destination station from the list or enter its name manually.
The system will then automatically calculate and display the fare for your chosen destination. Carefully verify that both the destination and the displayed price are correct before proceeding. After confirming, choose your preferred payment method—options typically include cash, credit or debit card, and mobile payment platforms such as Alipay or WeChat Pay.
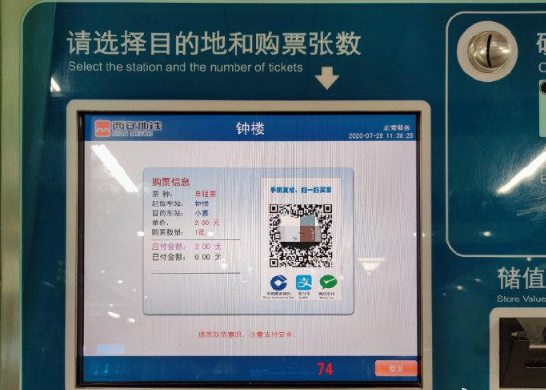
Once your payment is successfully processed, the machine will print out a paper ticket. Be sure to take the ticket and keep it with you throughout your entire journey, as you will need it to enter and exit the subway system. When you arrive at the subway entrance, tap your ticket on the card reader located at the turnstile; this will automatically open the gate and allow you to enter.

After reaching your destination, exit by inserting the ticket into the slot on the turnstile; the machine will collect your ticket and the gate will open to let you out.
Security Check and Entry
All passengers must undergo security screening before entering the subway station. You will be required to place any bags, backpacks, or personal belongings onto the conveyor belt for scanning by an X-ray machine.
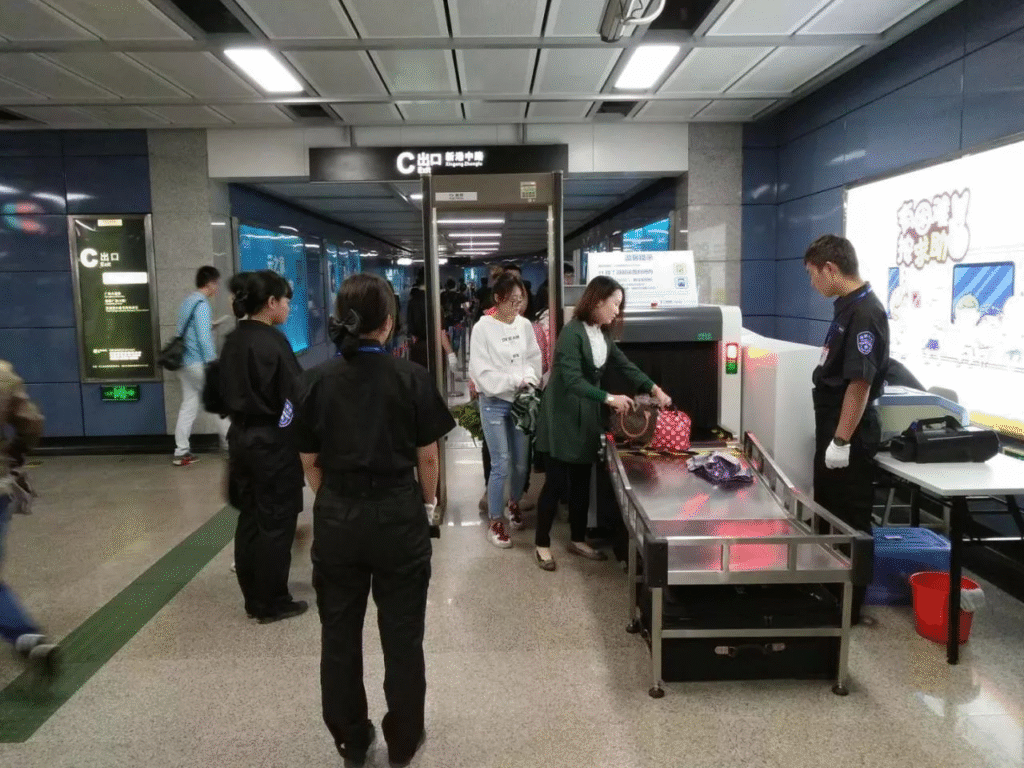

Please cooperate with security personnel during the inspection; if necessary, you may be subjected to additional screening using a handheld metal detector. After completing the baggage inspection, proceed to the turnstiles. Use the QR code on your mobile device or a physical card to scan the designated area on the turnstile, or tap your transit card on the card reader.

The gate will automatically open, allowing you to enter the subway platform area. Please ensure that your QR code or transit card is valid and clearly displayed to facilitate smooth entry.
Find Your Line and Direction
Each station is equipped with clear signage that indicates the line colors and directions of travel.

At major interchange stations such as Xizhimen and Dongzhimen, it is advisable to allocate additional time for transferring between platforms.
Transfers
Most interchange stations within the Beijing subway system are designed with convenient internal transfer passages. These allow passengers to move seamlessly between different lines without needing to exit the paid area or undergo security checks again, which significantly speeds up the transfer process and improves travel efficiency.
However, there are exceptions. For example, at stations like Beijing South Railway Station (北京南站), the transfer between lines may involve relatively long walking distances, sometimes requiring passengers to navigate through extensive corridors, escalators, or even multiple levels. In these cases, transfers can take significantly more time compared to other interchange stations.
Because of these variations, it is important to plan your transfer time carefully, especially if you have tight connections or are unfamiliar with the station layout. Consulting station maps, using official subway apps, or arriving earlier can help avoid rushing and ensure a smooth transit experience.
Exiting the Subway
Upon arrival at your destination station, follow the clearly marked signs for the “Exit.” To leave the subway system, simply scan your QR code or tap your transit card on the turnstile reader. Once recognized, the gate will open, allowing you to exit and complete your journey smoothly.
Tips for Travelers
- The first trains usually start running between 5:30 and 6:00 AM, and the last trains around 11:00 PM.
- Exact times vary by line.
- It is recommended to use the official “Beijing Subway” app or Gaode Maps (Amap) for real-time navigation and route planning.
- During peak hours (approximately 7:30–9:00 AM and 5:30–7:30 PM), trains may be very crowded. Try to avoid traveling during these times if possible.
Additional Notes
- Most ticket machines and turnstiles support contactless payments via mobile apps such as Alipay and WeChat Pay.
- Foreigners can also use these apps by linking their international credit cards or using special versions for tourists.
- Keep your ticket or QR code handy until you exit the system, as you will need it for the exit gates.
- In case of lost tickets, seek assistance at the station service counters immediately.
Conclusion
The Beijing Subway is not only the backbone of the city’s transportation network but also an indispensable tool for exploring Beijing. Whether you want to visit historic sites like Tiananmen Square, modern business districts such as Guomao and Wangjing, or academic hubs like Haidian, a single ticket or pass grants you access across the network.
This guide is designed to help you navigate the Beijing Subway efficiently. If you need personalized route planning or recommendations for attractions near subway stations, feel free to reach out for further assistance through our official website.